Obese patients who suffer complications after gastric bypass surgery may face further health risks because their weight exceeds the limits of diagnostic imaging equipment, according to a study presented November 27 at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America. In the study, approximately 27 percent of patients weighing more than 450 pounds needed imaging to diagnose a problem after surgery and could not be accommodated because of their size. "When patients weigh more than 450 pounds, standard diagnostic imaging often cannot be used," said Raul N. Uppot, M.D., an assistant radiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and instructor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston. "In these cases, physicians must resort to other means of diagnosis such as exploratory surgery or using less accurate or more invasive techniques."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, obesity has grown dramatically in the last 20 years. Today, nearly one-third of the American population is obese. Along with the rise in obesity among American adults has come an increase in the number of gastric bypass procedures performed.
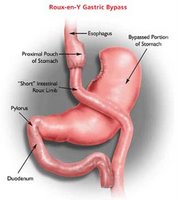
The American Society for Bariatric Surgery estimated approximately 140,000 gastric bypass procedures were performed in the United States in 2005. In a gastric bypass procedure, the stomach is surgically reduced, and part of the small intestine is bypassed. Like any surgical procedure, gastric bypass is not without risks. Most common complications include suture tears and leaks, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia and infection. Serious complications tend to be more prevalent among the severely overweight.
Dr. Uppot and colleagues conducted an eight-year retrospective study of all patients weighing more than 450 pounds who underwent a gastric bypass procedure at MGH between June 1999 and April 2007. Patient imaging usage and clinical course were tracked using electronic health records and evaluated to determine the outcomes of those who, based on their weight, were denied their physicians' first choice of imaging. The maximum weight limit for a computed tomography (CT) table is 450 pounds.
The researchers found that 12 (27 percent) of the 44 patients who weighed more than 450 pounds required postsurgical imaging because of a clinical condition, but were denied because they were above the weight restriction for the equipment. Four patients who could not be evaluated with imaging for suspected leaks were required to return for surgery.
Two additional patients with suspected lung blood clots could not undergo a chest CT. Of two patients who came in with nonspecific abdominal pain, one was evaluated with ultrasound and the other one had a barium swallow test. Because imaging was not an option, one patient who suffered trauma underwent exploratory surgery in lieu of noninvasive imaging. Another patient was denied a chest CT and received no further imaging evaluation.
"When obese patients cannot be diagnosed using standard-of-care imaging techniques, then other diagnostic measures have to be instituted," Dr. Uppot said. "Patient care may be ultimately affected due to a compromised diagnosis."
Dr. Uppot noted that the obesity trend cannot be ignored. "Unless major changes are made to the American diet or exercise habits, this is a problem that we will have to address," he said. "When an obese person is contemplating gastric bypass surgery, he or she should consider that they will need follow-up imaging but may not be able to get the appropriate tests."
Co-authors of the paper presented by Dr. Uppot are D.V. Sahani, M.D., D.A. Gervais, M.D., P.R. Mueller, M.D., P.F. Hahn, M.D., Ph.D., and S.I. Lee, M.D., Ph.D.
Adapted from materials provided by Radiological Society of North America.
gastric bypass surgery lawsuits